what are the ppe for welding

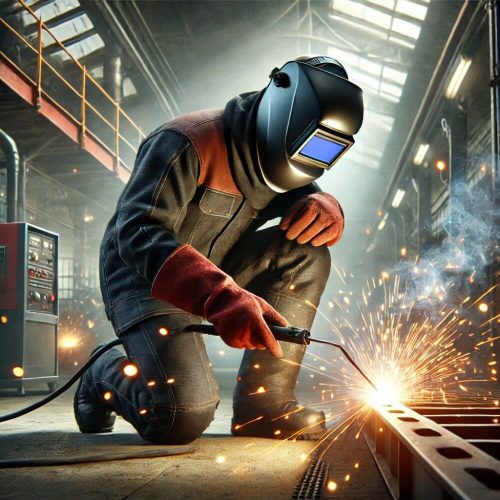
One sunny Sunday, Alex and his dad decided to build a metal shelf for Alex’s room. As his dad used a welder, Alex noticed he was wearing special gear like a shiny helmet and thick gloves. Curious, Alex asked why this equipment was so important. His dad explained that welding can be dangerous with hot metal and bright sparks, so PPE, or Personal Protective Equipment, is necessary to keep welders safe.
In this blog post, I’ll explore all the essential PPE items for welding. You’ll learn why each piece is important and how it helps welders work safely. Whether you’re curious about welding or just want to know how to stay safe in different activities, this guide will give you all the information you need. So let’s dive in and discover the amazing gear that protects welders every day!
What is PPE in Welding?
PPE stands for Personal Protective Equipment. In welding, PPE includes all the special clothes and gear that welders wear to keep themselves safe while working. Just like how superheroes wear suits to protect themselves, welders use PPE to guard against the dangers of welding.
Why is PPE Important in Welding?
Wearing the right PPE is very important for welders. Here are some reasons why PPE is essential:
-
Protects Eyes and Face:
- Welding Helmets: Shield the eyes and face from bright sparks and harmful light.
- Safety Glasses: Provide extra protection against flying pieces of metal.
-
Guards Against Burns:
- Gloves: Keep hands safe from hot metal and sparks.
- Protective Clothing: Prevents burns from hot sparks and flames.
-
Prevents Respiratory Issues:
- Respirators: Help welders breathe clean air by filtering out harmful fumes and dust.
-
Keeps Ears Safe:
- Earplugs or Earmuffs: Protect hearing from loud noises made by welding machines.
-
Protects Feet:
- Steel-Toed Boots: Guard feet against heavy falling objects and hot surfaces.

- Steel-Toed Boots: Guard feet against heavy falling objects and hot surfaces.
Rules and Standards for Welding PPE
To make sure everyone stays safe while welding, there are rules and standards that welders must follow. One important organization that sets these rules is OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration). OSHA helps create guidelines to protect workers from dangers on the job.
Here are some key points from OSHA’s rules about welding PPE:
- Eye and Face Protection:
- Welders must wear helmets or goggles that meet specific safety standards to protect against bright light and flying sparks.
- Hand and Arm Protection:
- Gloves made of fire-resistant materials must be worn to protect against burns.
- Body Protection:
- Protective clothing, such as jackets or aprons, should cover the skin to prevent burns from sparks and hot metal.
- Respiratory Protection:
- If welding creates harmful fumes or dust, welders must use respirators to breathe clean air.
- Hearing Protection:
- In areas with loud welding equipment, earplugs or earmuffs should be worn to protect hearing.
- Foot Protection:
- Welders need to wear sturdy boots with steel toes to protect their feet from heavy or hot objects.
- Welders need to wear sturdy boots with steel toes to protect their feet from heavy or hot objects.
Essential PPE for Welders
Welding is a cool way to join metal pieces together, but it can be dangerous too. That’s why welders wear special gear called Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) to stay safe. Let’s learn about the essential PPE items that help protect welders from harm.
Welding Helmets
Features and Benefits
- Protects the Face and Eyes: Welding helmets have a dark shield that covers the welder’s face and eyes. This shield blocks the bright light and sparks that come from welding.
- Reduces Glare: The dark glass helps reduce the bright glare, making it easier for welders to see what they are doing.
- Hides the Weld Area: When welders start welding, the shield automatically darkens to protect their eyes from the bright flash.
Types and Selection Tips
- Auto-Darkening Helmets: These helmets automatically get darker when welding starts. They are convenient because welders don’t have to flip the helmet up and down.
- Passive Helmets: These have a fixed dark shade and don’t change automatically. Welders need to lift the helmet to see before and after welding.
- Selection Tips:
- Comfort: Choose a helmet that fits well and is comfortable to wear for long periods.
- Protection Level: Make sure the helmet blocks harmful UV and infrared (IR) rays.
- Adjustable Features: Look for helmets with adjustable straps and settings to customize the fit.
Protective Gloves
Material Considerations
- Leather Gloves: These are strong and protect hands from heat and sparks. They are great for most welding jobs.
- Aluminized Gloves: Made with a special coating, these gloves protect against intense heat and are good for heavy-duty welding.
Different Types for Various Welding Tasks
- Basic Welding Gloves: Ideal for light welding tasks, offering good protection and flexibility.
- Heavy-Duty Welding Gloves: Used for more intense welding, providing extra protection and durability.
- Specialty Gloves: Some gloves are designed for specific types of welding, like TIG or MIG welding, offering tailored protection.
Protective Clothing
Importance of Flame-Resistant Materials
- Flame-Resistant Fabrics: These materials don’t catch fire easily, protecting welders from burns caused by sparks and hot metal.
- Layering: Wearing multiple layers helps keep heat away from the body and provides extra protection.
Suitable Garments for Different Welding Environments
- Welding Jackets: Made from thick, flame-resistant materials, these jackets protect the arms and torso.
- Welding Aprons: Worn over regular clothes, aprons offer additional protection for the front of the body.
- Sleeveless Vests: In some cases, welders might wear vests to allow for better movement while still providing protection.
Respiratory Protection
When It’s Necessary
- Breathing Clean Air: Welding can produce harmful fumes and dust. Respirators are needed to keep welders’ lungs safe.
- Toxic Fumes: Some welding jobs create dangerous gases that can cause health problems if inhaled.
Choosing the Right Respirator
- Half-Face Respirators: Cover the nose and mouth, filtering out harmful particles and gases.
- Full-Face Respirators: Cover the entire face, providing more protection and better visibility.
- Selection Tips:
- Fit: Make sure the respirator fits snugly to prevent harmful air from getting in.
- Filter Type: Choose the right filter for the type of welding you are doing to ensure maximum protection.
Eye Protection
Beyond Helmets: Safety Glasses and Goggles
- Safety Glasses: Protect the eyes from flying sparks and small debris. They are lightweight and comfortable.
- Welding Goggles: Offer more coverage than safety glasses, protecting the eyes from intense light and heat.
UV and IR Protection Specifics
- UV Protection: Blocks harmful ultraviolet rays that can damage the eyes.
- IR Protection: Shields the eyes from infrared rays, preventing eye strain and injury.
- Combined Protection: Some goggles and glasses provide both UV and IR protection for complete eye safety.
Hearing Protection
Necessity in Loud Welding Environments
- Loud Noises: Welding machines can be very loud, which can hurt welders’ ears over time.
- Noise Reduction: Hearing protection helps prevent hearing loss caused by constant loud sounds.
Options Available
- Earplugs: Small devices inserted into the ears to block out loud noises. They are easy to use and comfortable.
- Earmuffs: Cover the entire ear to reduce noise. They are reusable and provide strong protection.
- Selection Tips:
- Comfort: Choose hearing protection that is comfortable to wear for long periods.
- Effectiveness: Make sure the protection blocks enough noise to keep your ears safe.
Foot Protection
Types of Safety Boots
- Steel-Toed Boots: Have a strong metal cap on the toe to protect feet from heavy falling objects and sharp tools.
- Welding Boots: Made from thick leather and often include additional insulation to protect against heat and sparks.
Key Features to Look For
- Durability: Boots should be strong and last a long time, even with heavy use.
- Heat Resistance: Choose boots that can handle high temperatures and protect against burns.
- Comfort: Look for boots with good support and cushioning to keep feet comfortable during long welding sessions.
- Non-Slip Soles: Prevents slips and falls, keeping welders safe on slippery surfaces.
Proper Usage and Maintenance of PPE
Wearing Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is important, but using it correctly and taking care of it makes it even better. Here are some simple guidelines and tips to help welders keep their PPE in great shape.
Guidelines for Wearing PPE Correctly
Wearing PPE the right way helps keep welders safe. Follow these easy steps to make sure your gear works well:
- Wear the Helmet Properly:
- Adjust the Straps: Make sure the helmet fits snugly on your head. The straps should be tight enough to stay in place but not too tight to be uncomfortable.
- Cover Your Face: The dark shield should cover your entire face to protect your eyes and skin from sparks and bright light.
- Put on Gloves Correctly:
- Choose the Right Size: Gloves should fit well. They shouldn’t be too tight or too loose.
- Check for Damage: Look for any tears or holes before wearing them. Damaged gloves won’t protect your hands properly.
- Wear Protective Clothing:
- Cover Your Body: Make sure your jacket or apron covers all parts of your arms and torso.
- Layer Up: Wearing multiple layers helps keep you safe from heat and sparks.
- Use Respirators Properly:
- Seal the Mask: Make sure the respirator fits tightly around your nose and mouth. There should be no gaps where harmful fumes can enter.
- Check the Filters: Make sure the filters are clean and not clogged. Replace them if needed.
- Protect Your Ears:
- Insert Earplugs Correctly: If you use earplugs, push them in gently until they fit snugly.
- Wear Earmuffs Over Ears: Earmuffs should cover your entire ears without being too tight.
- Wear the Right Boots:
- Fasten the Laces: Make sure your boots are tied securely so they stay on your feet.
- Check for Comfort: Your boots should feel comfortable and supportive while you work.
Maintenance Tips to Ensure Longevity and Effectiveness
Taking good care of PPE helps it last longer and stay effective. Here are some easy tips to keep your gear in top shape:
- Clean Your Helmet:
- Wipe the Inside and Outside: Use a damp cloth to clean your helmet after each use. Remove any dirt or debris.
- Check the Shield: Make sure the dark shield is clean and free from scratches. Replace it if it gets damaged.
- Take Care of Your Gloves:
- Wash Regularly: Clean your gloves after each use to remove dirt and metal particles.
- Store Properly: Keep your gloves in a dry place away from direct sunlight to prevent them from wearing out quickly.
- Maintain Protective Clothing:
- Wash After Use: Clean your jackets and aprons according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Inspect for Damage: Look for any tears or worn-out spots. Repair or replace clothing that is damaged.
- Keep Respirators in Good Condition:
- Clean the Mask: Rinse the respirator with clean water and let it dry completely before storing.
- Replace Filters: Change the filters regularly or whenever they become dirty or damaged.
- Protect Your Ears:
- Clean Earmuffs and Earplugs: Wipe them down after each use to keep them clean and hygienic.
- Store Properly: Keep earmuffs and earplugs in a clean, dry place to prevent damage.
- Care for Your Boots:
- Clean After Use: Remove any dirt or metal scraps from your boots after welding.
- Dry Completely: Let your boots dry fully before wearing them again to prevent mold and bad smells.
- Check for Wear: Look for any signs of wear and tear, such as broken soles or loose stitching. Repair or replace boots as needed.
- Store PPE Safely:
- Organize Your Gear: Keep all your PPE in a clean, organized area. This makes it easy to find and use each item.
- Avoid Extreme Temperatures: Don’t store PPE in places that are too hot or too cold, as this can damage the materials.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even though PPE keeps welders safe, sometimes people make mistakes that can put them at risk. Here are some common mistakes to watch out for and how to avoid them.
Skipping PPE Usage
Why It’s a Bad Idea
- Gets You Hurt: Without PPE, welders can get burned by hot sparks or hurt their eyes from bright lights.
- Long-Term Health Problems: Not wearing PPE can lead to serious health issues over time, like breathing problems from harmful fumes.
- No Protection in Accidents: PPE helps protect welders during unexpected accidents. Skipping it means no backup protection.
How to Avoid This Mistake
- Always Wear Your Gear: Make sure to put on all your PPE before starting to weld.
- Make It a Habit: Get into the routine of wearing PPE every time you work. It should become second nature.
- Remind Yourself and Others: If you see someone not wearing PPE, gently remind them to put it on.
Using Damaged or Worn-Out Equipment
Why It’s a Bad Idea
- Less Protection: Damaged PPE doesn’t protect as well. For example, a cracked helmet shield won’t block sparks properly.
- Increased Risk of Injury: Worn-out gloves might have holes, letting hot metal touch your skin.
- Uncomfortable to Use: Damaged gear can be uncomfortable, making it harder to work safely.
How to Avoid This Mistake
- Regular Inspections: Check your PPE before each use. Look for any signs of damage like tears, cracks, or worn areas.
- Replace When Needed: If you find any damage, replace the PPE right away. Don’t use it until it’s fixed.
- Proper Storage: Keep your PPE in a safe place where it won’t get damaged. Avoid leaving it in hot or wet areas.
Improper Fitting of PPE
Why It’s a Bad Idea
- Doesn’t Stay in Place: If PPE doesn’t fit right, it can move around and not protect you properly.
- Discomfort: Poorly fitting gear can be uncomfortable, making it hard to concentrate on welding.
- Increased Risk of Accidents: If your helmet or gloves don’t fit well, you might not notice sparks or hot metal coming your way.
How to Avoid This Mistake
- Choose the Right Size: Make sure your PPE fits you well. It shouldn’t be too tight or too loose.
- Adjustable Features: Look for gear with adjustable straps or settings so you can customize the fit.
- Try It On: Before using new PPE, try it on to ensure it feels comfortable and stays in place.
Always make sure your PPE fits well and is in good condition. Take care of your gear by cleaning and checking it regularly. If something is damaged or doesn’t fit right, replace it right away. And never skip wearing your PPE, even if you’re in a hurry.
Safety is like a superhero’s shield—it protects you and lets you do amazing things without fear. So, whether you’re a young builder like Emma or someone who loves creating things, always prioritize safety by wearing the right PPE. Stay safe, have fun, and keep building your awesome projects!
FAQs
What is the most important PPE for welding?
Welding helmets are one of the most important pieces of PPE for welding. They protect your face and eyes from bright sparks and harmful light. Without a helmet, the bright flash from welding can hurt your eyes and skin. A good helmet helps you see clearly while keeping you safe from sparks flying around.
Can I use non-specialized gloves for welding?
No, you should not use non-specialized gloves for welding. Welding gloves are made from special materials like leather that can protect your hands from heat, sparks, and sharp metal pieces. Regular gloves, like cotton or synthetic ones, do not offer the same level of protection. Using the wrong gloves can lead to burns or injuries, so it’s important to wear gloves designed for welding.
How often should welding PPE be replaced?
Welding PPE should be replaced regularly to ensure it stays effective. Here are some guidelines:
- Helmets: Replace the dark shield if it gets scratched or damaged. Check the helmet every time you use it to make sure it’s in good condition.
- Gloves: If your gloves have holes, tears, or show signs of wear, get a new pair. Regularly inspect them for any damage.
- Protective Clothing: Wash your jackets and aprons after each use. If the fabric becomes worn or starts to tear, replace the clothing to keep yourself safe.
- Respirators: Change the filters as recommended by the manufacturer or if they become dirty. Replace the entire respirator if it gets damaged.
- Hearing Protection: Clean earmuffs and earplugs regularly. If they don’t fit well or are damaged, get new ones.
- Boots: Check your safety boots for cracks, worn soles, or other damage. Replace them if they are no longer protective.






